Why Your Digestive Health Is Your Secret Weapon for Better Energy, Immunity, and Mental Clarity
Understanding the Digestive System’s Role in Health
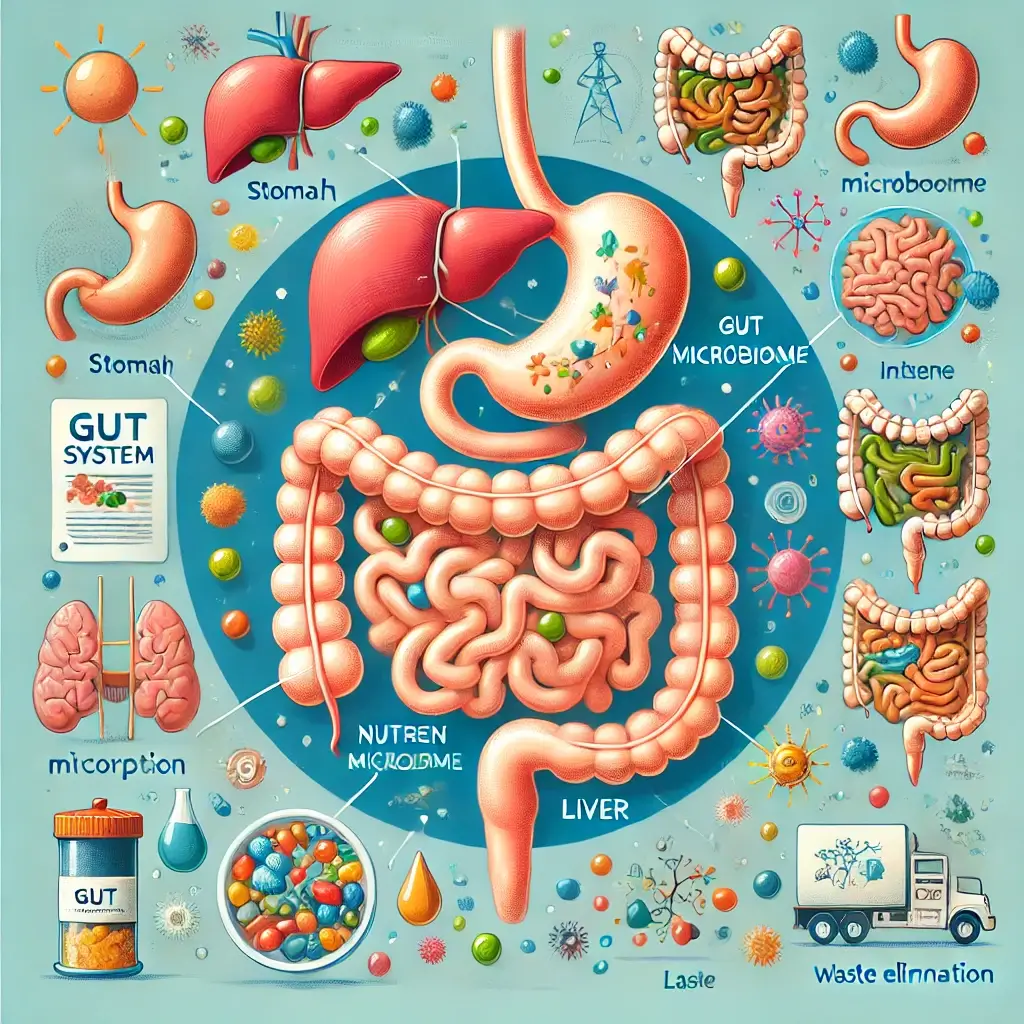
The digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering, ensuring the body receives the nutrients it needs to thrive while discarding what it doesn’t. This system encompasses multiple organs, each with a specific role in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. When operating smoothly, the digestive system is a powerful driver of energy, immunity, and overall health. However, its dysfunction can manifest in ways that significantly affect quality of life, from persistent fatigue to chronic discomfort.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Overall Wellness
Modern research continues to highlight the importance of digestive health in maintaining holistic well-being. The gut microbiome’s influence on immune function, a diverse ecosystem of microorganisms in the digestive tract, influences not only digestion but also immune function, hormonal balance, and even mood. Meanwhile, the gut-brain axis connection to mental health connects the digestive system and central nervous system, demonstrating how gut health can affect mental clarity and emotional resilience.
The Importance of Monitoring Digestive Health
Understanding the signs of a healthy digestive system is essential for everyone. These indicators serve as a barometer of overall health, helping individuals make lifestyle changes that support bodily processes. This article unpacks the hallmarks of optimal digestive health, the science behind them, and practical steps to foster a resilient digestive system.
Key Signs of a Healthy Digestive System
A healthy digestive system manifests through several observable signs. Scientific studies provide a deeper understanding of these indicators and their significance:
Understanding Normal Bowel Movement Patterns
Regular and Predictable Bowel Movements: Consistent bowel movement frequency and patterns are a cornerstone of digestive health. The Digestive Diseases and Sciences journal defines a normal frequency as anywhere from three times daily to three times weekly. Beyond frequency, the predictability and ease of elimination are crucial. Straining or irregularity may point to dietary deficiencies or stress, signaling the need for intervention.
Characteristics of Healthy Stool
Healthy digestion produces well-formed stools that are easy to pass. The Bristol Stool Scale identifies Types 3 and 4 (banana-shaped and smooth, sausage-like) as ideal. A 2016 study in Diseases of the Colon & Rectum linked these stool types to efficient gut motility and nutrient processing, while harder or looser stools can indicate imbalances or irritation.
Understanding Digestive Comfort Levels
Gas and bloating are natural byproducts of digestion, especially after consuming fiber-rich foods or carbonated beverages. However, excessive bloating and digestive discomfort may signal underlying issues such as food intolerances or dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut bacteria. Research in Nutrients highlights the role of probiotics and a diverse microbiome in mitigating these symptoms.
The Role of Nutrient Absorption
The gut lining plays a critical role in nutrient absorption, ensuring the body benefits fully from the foods consumed. Compromised nutrient absorption and deficiencies, as noted in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, can result in deficiencies in key vitamins and minerals, leading to symptoms such as brittle nails, fatigue, or weakened immunity.
Energy Levels and Digestive Health
A well-functioning digestive system ensures consistent energy throughout the day by efficiently converting food into usable fuel. Studies in Gut associate a diverse microbiome and metabolic efficiency with improved metabolic efficiency and reduced risk of energy crashes, emphasizing the importance of gut health in maintaining vitality.
The Impact on Mental and Emotional Health
The gut’s influence extends far beyond digestion, thanks to the gut-brain axis. Research in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology underscores the link between digestive health and cognitive function, cognitive function, and sleep quality. A balanced microbiome contributes to reduced stress, improved focus, and better overall emotional health.
Supporting Digestive Health Through Lifestyle
Supporting a healthy digestive system requires intentional habits and lifestyle choices:
Dietary Modifications: Prioritize fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Incorporate fermented foods like kimchi, miso, and yogurt for their probiotic benefits.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration for digestive health ensures smooth digestion and prevents constipation. Drinking at least 8–10 glasses of water daily is essential.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes gut motility and helps regulate bowel movements. Even moderate exercises, such as walking, can significantly benefit digestion.
Stress Management: Chronic stress impact on digestive health can disrupt the gut-brain axis, leading to issues like IBS or heartburn. Mindfulness practices, deep breathing, and yoga can mitigate stress-induced digestive disruptions.
Consult a Professional: Persistent digestive discomfort or irregularities warrant professional evaluation to rule out conditions like IBS, Crohn’s disease, or food sensitivities.
Final Thoughts on Digestive Wellness
The digestive system is a dynamic and multifaceted network, central to both physical and emotional well-being. Recognizing the signs of a healthy digestive system and optimal function, such as regular bowel movements, ideal stool form, minimal bloating, efficient nutrient absorption, and sustained energy, empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward optimizing their health. By incorporating a fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, exercising, and managing stress, you can create a foundation for lifelong digestive wellness. Remember, chronic digestive issues are not to be ignored; they require professional guidance for diagnosis and treatment. A healthy digestive system not only fuels the body but also uplifts the spirit, ensuring a life of vitality and resilience.